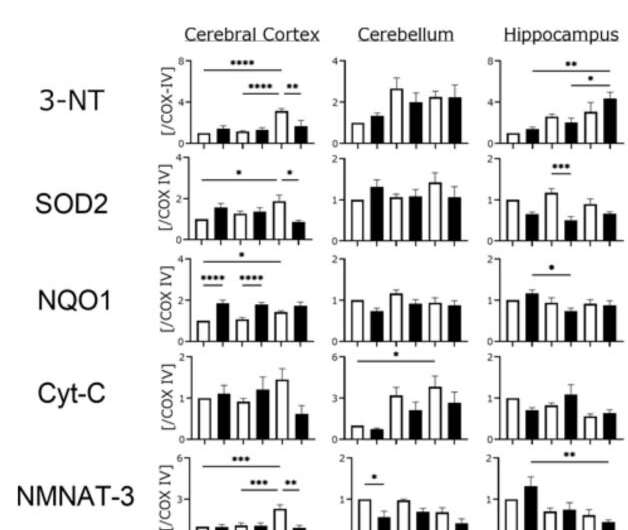
The mitochondrial electron transport chain, which is required for generating energy during cellular processes, also produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) that attack tissue and cause oxidative damage. This damage can cause mitochondrial dysfunction and even lead to cell death. Since our brain uses more oxygen than other organs, it is more vulnerable to this ROS damage.
According to literature, ROS also causes the buildup of amyloid-β (Aβ), which marks the onset of…


























