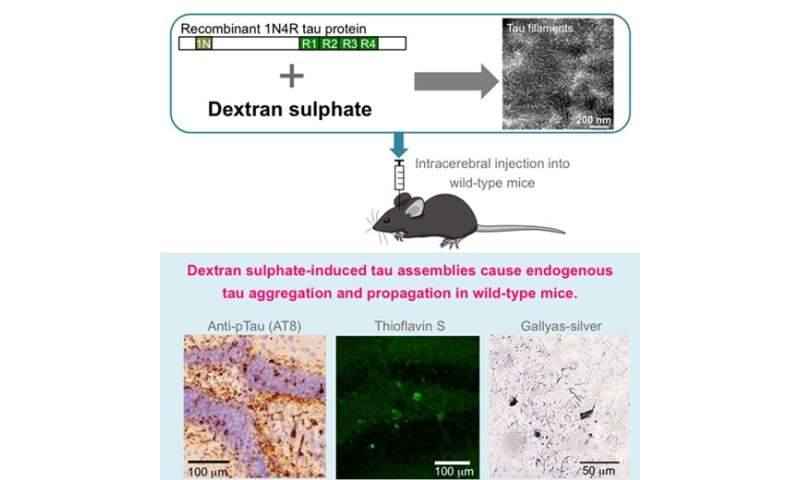
Accumulation of assembled tau protein in the central nervous system is characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease and several other neurodegenerative diseases, called tauopathies. Recent studies have revealed that propagation of assembled tau is key to understanding the pathological mechanisms of these diseases. Mouse models of tau propagation are established by injecting human-derived tau seeds intracerebrally; nevertheless, these have a limitation in terms of regulation of availability of human samples. To date, no study has shown that synthetic assembled tau induce tau propagation in non-transgenic mice.
…


























