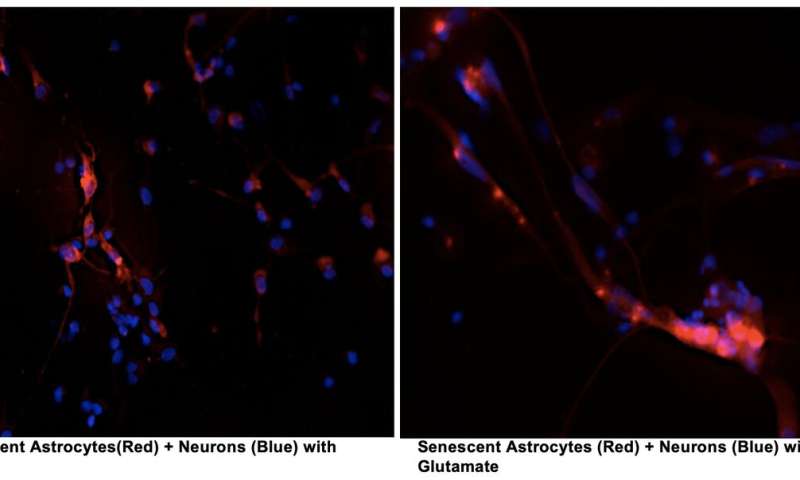
Although a link has been established between chronic inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases, there have been many open questions regarding how cellular senescence, a process whereby cells that stop dividing under stress spew out a mix of inflammatory proteins, affects these pathologies. Publishing in PLOS ONE, researchers at the Buck Institute report that senescence in astrocytes, the most abundant cell type in the brain, leads to damaging “excitotoxicity” in cortical neurons that are involved in memory.
…


























