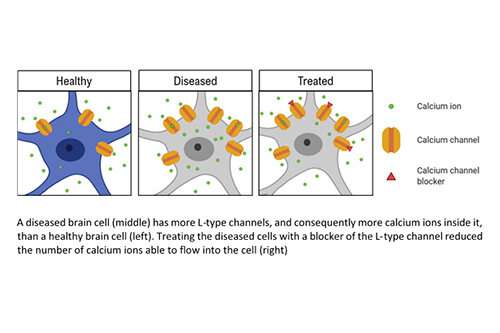
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia but the changes in brain cell function underlying memory loss remains poorly understood. Researchers at the University of Bristol have identified that calcium channel blockers may be effective in treating memory loss.
The team’s findings, published in Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, found treating a diseased brain cell with a blocker of the L-type channel reduced the number of calcium ions able to flow into the brain cell.
The researchers used fruit flies to study AD, using a fluorescent molecule called GCaMP6f, which reports the amount of calcium…

























