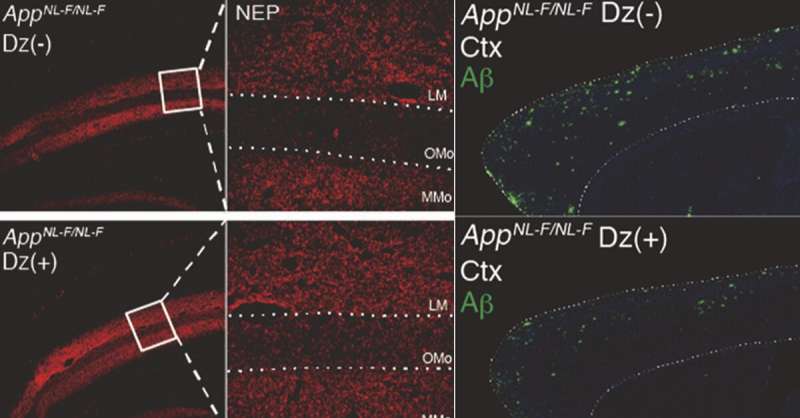
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan have discovered that the protein α-endosulfine (ENSA) is involved in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Studies in mice showed that eliminating this protein entirely or using drugs to block its function reduced physical changes in the brain associated with the disease and improved memory. Drug therapy that aims to block ENSA activity could be a more effective treatment than what is currently available, as well as being…



























