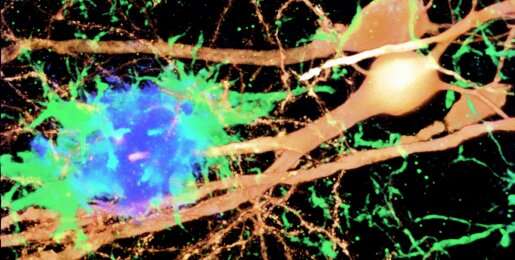
When immunologist Dr. Wei Cao joined Baylor College of Medicine three-and-a-half years ago, her first project was to investigate how inflammation contributes to Alzheimer’s disease.
“Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. The current understanding is that, in addition to having beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles, the brains of patients with this condition have a marked inflammatory response, and that this inflammation might be more of a…


























